2023 GBENN Virtual Summit

Summit Day 1: November 28, 2023 – Equity and Environmental Justice in Green Business Programs
This day will focus on highlighting programs that are integrating equity and environmental justice into their work to support businesses in disadvantaged or underserved communities. We will learn about two distinct initiatives and then discuss existing work and ideas in small group sessions, helping us all increase our reach to serve more businesses located in underserved communities.
2pm ET: Welcome! Introductions and Networking
2:30pm ET: Small Business Equity Fund – Colorado Green Business Program
- Session Speaker: Francis Otero, Green Business Specialist, Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment.
The Colorado Green Business Network launched the Small Business Equity Fund (SBEF) grant pilot program in Aurora, Colorado. The program provides funding to small businesses interested in implementing energy efficiency upgrades. This Equity Fund focuses on supporting businesses in disproportionately impacted communities. The program offers the free replacement and installation of LED lighting, programmable thermostats, occupancy sensors, and walk-in cooler motors. It also provides a cost-share cover of the installation of commercial refrigeration equipment replacements. Learn more about the pilot and its successes in its first year!
3:45pm ET: Business Vulnerability Index & Map – Illinois Green Business Program
- Session Speaker: Cassie Carroll, Program Director, Illinois Green Business Program & the Smart Energy Design Assistance Center at UIUC
The Smart Energy Design Assistance Center (SEDAC) at UIUC and the California Green Business Network collaborated to develop a map that can help green business programs more easily identify businesses that are vulnerable to climate, environmental, economic, and socioeconomic impacts. The map combines untraditional datasets and weight priorities to identify businesses that may be impacted by a multitude of factors and sub-factors. Learn about why the map was created, how to use it, and resources to reach businesses in underserved communities across the U.S.
4:40pm ET: Breakout Sessions and Discussion
5:25pm ET: Day 1 Recap and Day 2 Preview – Thank you!
Summit Day 2: November 29, 2023 – Green Business Program Innovations & Trends
This day will focus on best practices, tools, and systems to help green business programs thrive. The Summit schedule will have room to foster dialogue amongst attendees through networking, breakout sessions, and discussion. We will ask all attendees to share an overview slide of their program to help get to know your program and its goals.
2pm ET: Welcome! Introductions and Networking
2:30pm ET: The Green Masters Program – Sustainability Management Tool for Businesses
- Session Speaker: Christa Kananen, Program Manager and Consultant, Wisconsin Business Sustainability Council
The Green Masters Program is a web-based sustainability management tool, currently used as a recognition program for WI businesses but expanding into a range of applications to help manufacturers and other businesses get started in sustainability by meeting them where they are and offering a roadmap for progress. This presentation will demonstrate the tool and provide context for how it can be leveraged to support manufacturers across the United States and beyond.
-
- Participants will learn:
- How to engage and support sustainability initiatives in manufacturing.
- How sustainability trends are impacting manufacturers (supply chain and ESG disclosure).
- How Green Business organizations can help, using the Green Masters Program as a tool.
3:45pm ET: Tools and Program Innovations for Green Business Programs
Small businesses are still recovering from the pandemic and face new challenges than they did before. This session will encourage sharing is a time to share and get advice from each other on what our challenges are and how we can overcome them to meet both our business’ needs and our funder’s needs. We’ll have a couple of green business programs share what they are seeing in their regions and how they are addressing the needs of their businesses through tools and program innovations.
Session Speakers:
- Using Surveys for Emissions Data Collection – Alyssia Chinda, Green Business Specialist, Colorado Green Business Network
- Developing Stepping Stones to Meet Businesses at any Sustainability Level – Illinois Green Business Program and SEDAC at UIUC
4:15pm ET: Breakout Sessions and Discussion
4:45pm ET: All-Group Sharing
5:25pm ET: Summit Wrap Up – Thank you!
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2021 Summit
GBENN 2021 Summit
The 4th National GBENN Summit was held virtually on September 8, 9 and 10, 2021 from 11am CT – 2pm CT daily. Thank you to greenUP! and Western Nevada College for their sponsorship and making this event possible.
GBENN is the nation’s hub for small business sustainability. The Summit is an opportunity for networking and sharing best practices among people who manage and operate green business programs or those that work with businesses to reduce environmental impact.
Summit Session Recordings and Slides
Day 1: September 8, 2021
Click here for Day 1 recording!
11:00am CT: Welcome and Keynote Speaker: Andrew Behar, CEO, As You Sow
Presentation Slides
Andrew Behar is the CEO of As You Sow, the nation’s leading non-profit practitioner of shareholder advocacy and engagement. Since 1992, As You Sow has used shareholder power to align investments with values and compel companies to reduce material risk on issues including climate change; toxins in the food system; ocean plastics; diversity, equity, and inclusion; racial justice; and wage equity.
Mr. Behar will focus on how major corporations are working to address climate and racial equity initiatives in their corporations and the importance of disclosing information to the general public. He will discuss As You Sow’s Racial Justice Scorecard and share stories of how corporations are facing their truths while putting plans in place to improve environmental, social and governance aspects of their organizations.
11:45am CT: Sustainability, Business Recovery and Resilience: Supporting Businesses During the Pandemic
This session will focus on how programs that support small and medium-sized businesses pivoted their sustainability programs and services to support business recovery, resilience and sustainability as the pandemic emerged. Learn how these programs have helped businesses access vital resources and funding, while building trust and resilience through sustainable business programs and incentives. We’ll also explore how small businesses can play a role in shaping policy that is attainable and provides support needed for community-wide adoption. Speakers in this session include:
12:55pm CT: Science-Based Climate Targeting and Data Management for Small Businesses
The time window in which to avoid the worst impacts of climate change is rapidly closing and massive action is needed by all aspects of society, including the small and medium sized businesses. While major corporations are setting science based GHG reduction targets in increasing numbers, this movement has yet to take hold in smaller businesses. In this session, we’ll explore how campaigns to address science-based climate targets for small business can be effective in addressing climate goals and discuss how programs are managing and sharing this data. Speakers in this session include:
_________________________________________________________
Day 2: September 9, 2021
Click here for Day 2 recording!
11:00am CT: Welcome and Keynote Speaker: Jarami Bond, Chief Storyteller, Bond Studio and Senior Advisor, GreenBiz.org
Featured as a 2017 GreenBiz 30 Under 30, Jarami is Chief Storyteller at Bond Studio, a visual storytelling company focused on helping companies, nonprofits, and entrepreneurs build their brands, engage their audiences, and unlock the power of their stories. Jarami also serves as Senior Advisor at GreenBiz.org, advocating for greater BIPOC representation and a deeper focus on social and environmental justice within the sustainability movement.
Mr. Bond will cover how we can build mutually-beneficial relationships that address BIPOC community needs and how to best adapt our programs or services to meet those community needs. He will discuss the best ways to partner with BIPOC communities and organizations to create more space and dialogue around sustainability and the clean economy.
11:45am CT: Advancing Equity through Sustainable Business Programming
In this session, we’ll explore successes, lessons learned, and best practices shared by four programs that have developed services in partnership with community organizations that both advance equity and meet sustainability goals for businesses. Each speaker will discuss their best approaches for building trust with community-based organizations, share program success stories, and highlight key strategies to advance equity initiatives in your community. Speakers in this session include:
- Daniel Schoonmaker, Executive Director, West Michigan Sustainable Business Forum – Presentation Slides
- Berenice Garcia-Tellez, Economic Sustainability Specialist, Longmont Sustainable Business Program, CO – Presentation Slides
- Elizabeth French, Business Sustainability Team Lead, Partners for Clean Environment (PACE), Boulder CO – Presentation Slides
- Maria Corona, Bilingual Sustainability Analyst, California Green Business Network (CAGBN) – Presentation Slides
- Brooke Wright, Strategic Initiatives Manager, Environmental Innovations – Presentation Slides
1:15pm CT: Increasing Access to US EPA Safer Choice-Certified Products
This session will highlight the opportunities and innovative collaborations ongoing to increase the access to US EPA Safer Choice-Certified products, especially in low-income and traditionally underserved communities. Panelists will introduce the EPA Safer Choice Program, discuss how small businesses are pursuing Safer Choice Certification and how green business programs can help increase the purchase and use of safer chemical products through a variety of tools. Speakers in this session include:
- Kat Compton, Pollution Prevention Coordinator, US EPA Region 10 – Presentation Slides
- Brittney Wendell, Associate Director, Pacific Northwest Pollution Prevention Resource Center – Presentation Slides
- Lisa Cox, Senior Toxics Reduction Analyst, Oregon Department of Environmental Quality – Presentation Slides
- Peter Cook, Director of Programs & Collaborations, Ecology Action – Presentation Slides
- Julia Presar, Residential Services Program Manager, King County Hazardous Waste Management Program, WA – Presentation Slides
- Katie Fellows, Project Manager, Research Services Team, King County Hazardous Waste Management Program, WA – Presentation Slides
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Day 3: September 10, 2021
Click here for Day 3 recording!
11:00am: Welcome and Keynote Speaker: Suzanne Shelton – Shelton Group
Presentation Slides
Suzanne Shelton is the voice and the vision of Shelton Group. Drawing on her extensive experience in energy and the environment – and 25+ years in the marketing and advertising industry – Suzanne provides high-level strategic insights for our clients and guidance for our research and creative departments.
Ms. Shelton will share her insights around customer attitudes towards sustainability and ESG initiatives in businesses across the country. Her session will provide insight on how we can pitch sustainability and ESG initiatives to businesses from a customer perspective and alert us of the latest data on consumer commitments and interest in sustainability in business.
12:15pm: Marketing Green Business for the New Millenia
Building a community of sustainable businesses can increase adoption of environmental practices, facilitate networking opportunities and encourage other businesses to join your program. In this session, panelists will discuss key marketing strategies to reach underserved businesses, build opportunities for businesses in your program to connect, and how to maintain communication with your business network. We’ll also dive into marketing campaign design, metrics and results, providing a number of ways your program can amplify all-star businesses while also increasing program participation. Whether you launch a Google AdWords campaign or test your e-newsletter subject line for better readership, you’ll walk away from this session with a plethora of new ideas on how to reach new businesses and build a great sustainable business community.
12:55pm: Aligning Regional and Local Programs with National Climate Goals
This session will provide an overview of how sustainable business programs and regional EPA representatives collaborate to drive climate impacts locally and regionally. This panel will reflect on upcoming national directives and how regions are planning to address those goals. We’ll explore how sustainable business programs and technical services can align with EPA climate initiatives, as well as uncover opportunities for regional partnerships to advance climate reduction goals locally, regionally, and nationally.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Virtual Summit Sponsors




Goals for the 2021 Summit
- Explore how all programs can support diverse small businesses in sustainable practices
- Strengthen the dialogue and advance collaborative opportunities that began at the 2013 Summit and continued during the 2016 and 2018 Summits
- Share best practice information across programs and foster collaboration that advances the unique objectives of green business programs
- Engage new green business engagement programs in the network, fostering networking and relationship-building between programs
2018 Summit Information
The 3rd National GBENN Summit occurred on November 8-9, 2018 at the Museum of Science and Industry in Chicago, Illinois. Over 35 green business programs that were interested in networking, learning, and sharing best green business engagement strategies for success attended. Thank you to the Museum of Science and Industry for donating space for the event and hosting the GBENN Summit. Thank you also to our Keynote – Aaron Stash – United Eco-Skies, to greenUP! in Nevada and the Illinois Green Business Association for hosting this year’s event

 2018 Summit Agenda and Presentations
2018 Summit Agenda and Presentations The 2018 Summit Agenda and Speaker Bios can be found here.
The 2018 Summit Agenda and Speaker Bios can be found here.
Keynote Presentation: United Eco-Skies –Aaron Stash – Manager, Environmental Strategy and Sustainability
Aaron Stash – Manager, Environmental Strategy and Sustainability, will be joining us to discuss how United is committed to operating sustainably and responsibly. This commitment means we strive to minimize the environmental impacts associated with our operations and continuously look for ways to reduce our footprint in the air, on the ground and at our facilities. Aaron will speak about their biofuels program in Los Angeles, as well as many other initiatives United has taken on to reduce their impact in the air and on the ground each day.
To learn more about United Eco-Skies before the Summit, click here.
Session 1: “Building Collaborative Community Partnerships that Bolster Funding and Build Program Capacity”
Session 2: “Listen to your Business Community – Adapting Program Models to Meet Business Needs and Interests”
Session 3: “Comparing Two Regional Program Models – Engaging and Sharing Business Participants Across Partners and Synergistic Community Programs”
Session 4: “Building Standards and Adjusting Your Program to Serve Unique Business Sectors”
Session 5: “Focus on Impact and Efficiency, Not Waste! Engaging Large Facilities and Major Events in Resource Reduction Best Practices”
Session 6: “Marketing and Business Recruitment – Strategies for Business Recruitment while Maintaining your Program Brand and Presence in the Community”
2016 Summit Information
The 2016 Summit was held on October 19th and 20th in St. Louis, MO. Below is the agenda and presentations from the event:
Conference Day 1: Wednesday, October 19, 2016
8:30am – 9:30am: Keynote Presentation – Dominick Brook, US Leader – Global Sustainability Tax Services, Ernst and Young
Ernst and Young has a rich portfolio of sustainability services for corporations across the world. Mr. Brook has been instrumental in creating programming utilizing incentives for businesses to implement sustainable activities within corporations. However, a national and global trend around corporate carbon taxes and trade might be on the horizon. Mr. Brook will address how corporate carbon tax markets are coming about in states across the U.S. and how green business programs can work within their communities, municipalities and businesses to address energy efficiency using carbon taxes.
9:45am – 11:30am: Session 1 – Formulas for Success: How to Efficiently Work with Small Businesses and Local Municipalities
Green business engagement programs use a wide variety of models to serve their local business population. Whether it be interns, cohorts of business participants, partnerships, or accreditation frameworks, each green business engagement program is unique. Learn from four very different green business engagement programs about their model and how they efficiently work with small businesses and/or local municipalities to drive environmental reduction in their communities.
11:30am – 12:20pm: Session 2 – Recognition – Elevating the Value of your Program through a Badge System
Recognition is one of the key benefits and reasons why businesses participate in green business engagement programs. The Illinois Green Business Association will discuss its new certification badge system: why and how it was developed, benefits of the new system, lessons learned, and how to develop one for your own program.
- Anthony Santarelli – Director, Illinois Green Business Association
12:30pm – 2:00pm – Lunch and Tour of the Missouri Botanical Garden
2:30pm – 3:30pm: Session 3 – Sustainability Reporting and Metrics
Collecting environmental metrics from businesses can be a challenge, but organizing and aggregating that data can prove to be an even bigger hurdle. Learn from the California Green Business Network and the Vancouver Economic Commission on how they use interactive platforms to manage green business metrics, identify industry trends, and provide real-time data on green business environmental outcomes in their programs.
3:30pm – 4:30pm: Session 4 – Leveraging Collective Impact to Address Community Climate and/or Environmental Goals
Community-wide partnerships can increase collective environmental reduction, provide collaborative service offerings, and engage more businesses in environmental efforts. Learn about how two organizations deployed community-wide sustainability programs that increased their impact and participation through leveraging their regional and/or local networks and successfully engaged businesses in the process.
4:30pm -5:00pm: Day 1 Wrap-up
6:30pm – 9:00pm: Networking Reception for Green Business Programs
GBENN’s networking event is at Schlafly Bottleworks in the Green Dining District certified restaurant in Maplewood, MO. The band that will be playing is Miss Jubilee and the Humdingers – this is a great local swing band. Part of the nation’s first Green Dining District, this indoor-outdoor venue in a recycled supermarket is a cultural and social anchor of the thriving business district in historic Maplewood, MO.
Conference Day 2: Thursday, October 20, 2016
8:30am – 9:30am – EPA Environmental Stewardship Resources – Benefits for Every Green Business Program
There are a number of resources that green business programs can use to help meet program goals. Some of these programs include Energy Star, US Green Business Counsel’s Leadership in Energy & Environmental Design (LEED), Green Schools and others. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has a number of sophisticated programs that are business friendly, free to use, measurable, and reap significant results. In a panel, EPA representatives will talk about how any green business program can leverage resources in EPA’s ENERGY STAR, Safer Choice, Food Recovery Challenge, and Waste Wise. EPA staff will also discuss data system management opportunities that GBENN members can use to measure both participant and whole program outcomes.
9:30am – 10:30am: Session 5 – Reaching New Industries that Do Not Have Existing Sustainability Standards
Staff from Certifiably Green Denver, the green business program for the City and County of Denver, Colorado will share their strategies for working with the emerging cannabis industry. Certifiably Green Denver is utilizing existing green business program staff and resources to navigate the unique challenges and opportunities this new industry presents.
- Emily Backus – Sustainability Advisor, City & County of Denver
10:30am – 11:30am: Session 6 – Evolving a Green Business Program in a Saturated Marketplace
As sustainability has hit mainstream media and major corporations, there has been an increase in organizations and communities launching efforts address climate change and decrease overall community and/or regional environmental impact. As these new programs take the spotlight, how can your green business program maintain visibility and uniqueness, while working with these new partners? Learn from our presenters on how this issue has been addressed in their cities and regions.
“Unifying green business programs under an umbrella brand to better serve business customers and maximize results.”
11:45am – 1:45pm – GBENN Development Session with Lunch
- How do we help foster growth within individual programs? What are those activities?
- How do we grow awareness of our collective impact?
- How can we become more nationally engaged as a collective group?
- Discuss overall Network structure and membership
1:45pm – 2:00pm: Wrap up and depart
3:00pm – 5:00pm: (Optional) Tour of University City Loop Green Dining District
2013 Summit Information
The first National Summit on Green Business Engagement Programs drew over forty leaders from across the United States to Boston on May 9 and 10, 2013. The Summit provided a forum for leaders to share achievements, discuss challenges, and exchange best practices for engaging the business community, partnering with local governments, collaborating with utility districts, and delivering program services. The summit was highly successful in identifying the critical factors for green business programs to support economically vibrant and sustainable cities where current and future generations will want to live, work, and play. The summit was organized by A Better City and facilitated by the Consensus Building Institute.
Participants were welcomed by Rick Dimino (President and CEO, A Better City), Brian Swett (Chief of Environment and Energy for the City of Boston) and Mariella Puerto (Senior Program Officer, Barr Foundation). These leaders stressed the importance of efforts to encourage businesses to reduce their environmental impact voluntarily through education and a little healthy competition. Throughout the event, participants told stories about their programs and shared lessons learned.
Download the Full 2013 Summary








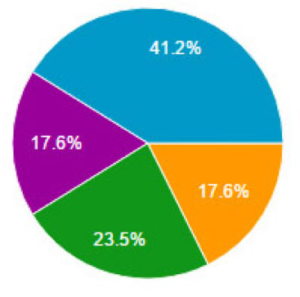

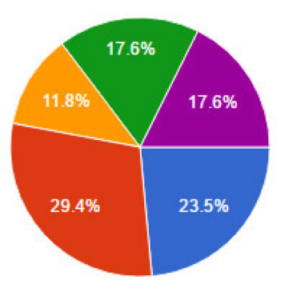


 The most challenging aspects of managing or executing green business programs are:
The most challenging aspects of managing or executing green business programs are: